China is a landlocked country with the longest coastline in the world. The characteristics of wind speeds on land and along the coast are entirely different, and typhoons pose significant risks to coastal wind turbines. Therefore, it's essential to develop distinct wind energy technologies tailored for each environment. Land-based wind turbines should focus on optimizing performance in low wind conditions, while coastal turbines must be designed to withstand high wind speeds and typhoon forces. This means that the design and appearance of these turbines will vary significantly. Only by addressing these differences can we maximize wind energy utilization in both land and coastal regions, ensuring longer operational times and stable, large-scale power generation. This approach will help fully leverage China’s vast wind resources and support the sustainable growth of its wind power industry.
To achieve this, we need to develop new types of wind turbines: one efficient for low-wind areas on land, and another capable of withstanding typhoons along the coast. Large-scale wind farm construction is a key initiative in China, with unique challenges compared to global standards. To tackle these issues, we plan to implement smart thermal power plants as backup systems, using inertial energy storage and advanced control technologies to manage the grid effectively.
Currently, wind power accounts for only a small share of China’s electricity supply. Despite the huge market potential, many manufacturers are underutilizing their capacity due to overproduction and grid constraints. However, the real opportunity lies in expanding wind turbine deployment across remote areas such as mountainous regions, grasslands, border posts, islands, and industrial sites. These locations have immense potential for wind energy development. If properly tapped, they could drive demand for large-scale wind equipment, helping to absorb excess production and even create new capacity.
China has limited land wind speeds, but there are many remote areas with potential. Existing wind turbines, developed for high-speed maritime environments, are inefficient on land, often failing to generate power below level 3 winds. Their high cost also limits widespread adoption. To address this, we must develop more efficient, low-cost turbines that can start generating power at lower wind speeds, operate reliably, and be affordable for widespread use.
For coastal areas, the challenge is designing wind turbines that can withstand typhoons. Current offshore technology has not yet solved the issues of blade strength and control system reliability. Typhoons have caused significant damage to wind farms in the past, highlighting the need for stronger, more resilient designs. One solution is to use smaller blades that reduce wind load, paired with multiple units to maintain efficiency. Additionally, improving control systems to respond faster to sudden changes in wind direction and speed is crucial.
Large-scale wind farms pose a major challenge for grid stability due to the unpredictable nature of wind. Sudden surges in power can destabilize the grid, especially when wind speeds fluctuate rapidly. To mitigate this, we propose integrating smart thermal power plants that act as buffers, absorbing excess power during peak times. This hybrid approach will enhance grid reliability and support the integration of renewable energy sources.
In summary, developing specialized wind turbines for different environments, improving control systems, and creating smart grid solutions are essential steps toward achieving a stable, efficient, and scalable wind power industry in China.
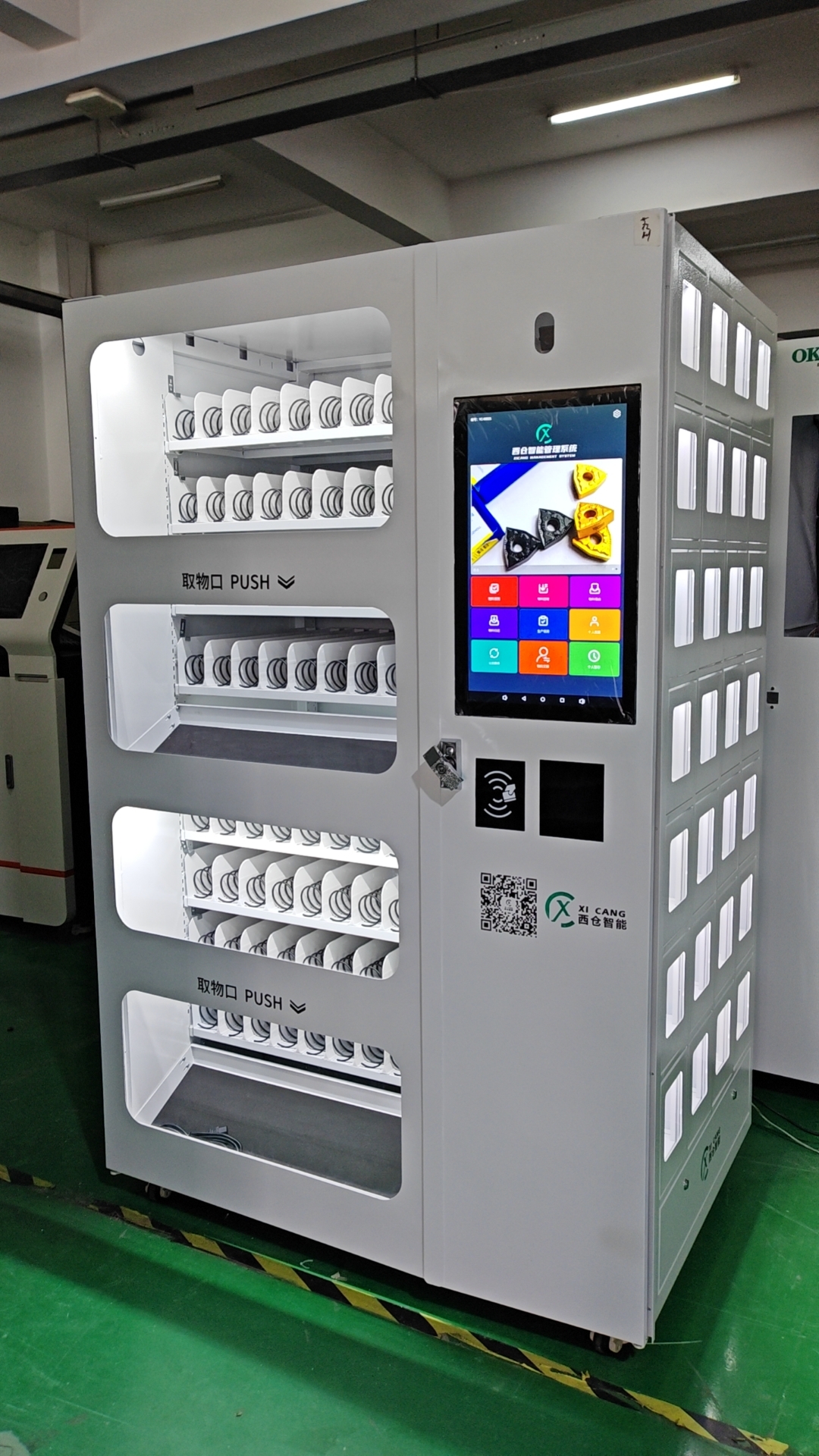
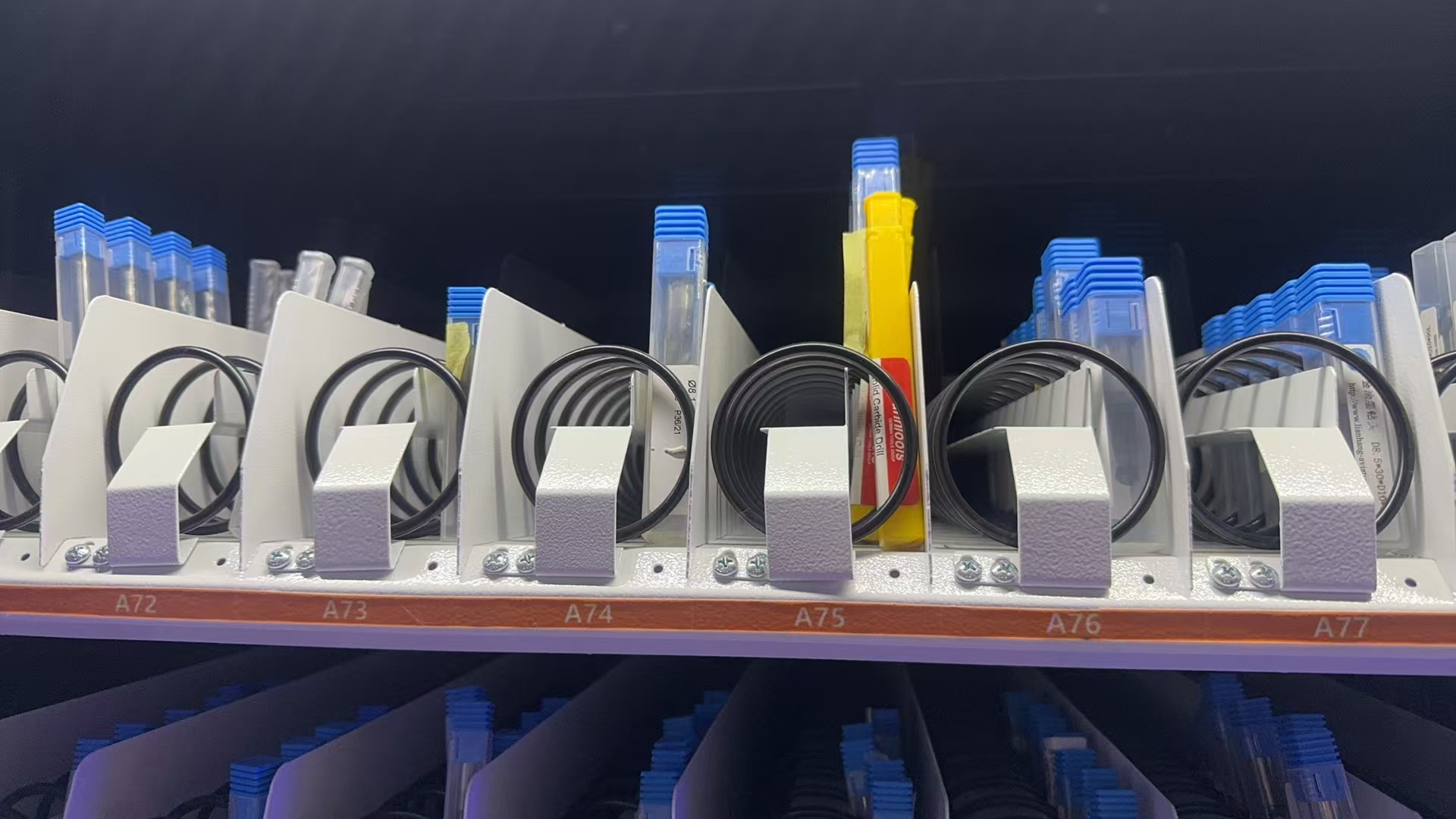
Dual Access Smart Coil & Grid Cabinet
Two dispensing ports for faster, smarter tool distribution
This cabinet combines spring coils and grid compartments with dual access windows, allowing two users to pick up items at the same time. It improves efficiency in busy workshops while maintaining full control over access and inventory.
Each side can be configured independently, supporting different item types such as boxed cutting tools, inserts, gloves, or small parts. With smart access control (RFID, face, code), real-time inventory tracking, and modular design, it’s ideal for factories with high tool turnover.
Applications:
CNC workshops, toolrooms, consumable management in production lines.
Highlights:
Dual user access, mixed storage modes, fast tool dispensing, customizable layout, real-time tracking.
Intelligent Workside Tool Cabinet,Intelligent Tool Handle Management Cabinet,Intelligent Labor Protection Equipment Management Cabinet,Intelligent Tool Management Cabinet
Jiangsu Xicang Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.xciwarehousing.com