Plastics make traditional materials unmatched in terms of plasticity, durability and chemical stability, so they are widely used in industrial production and daily life. According to statistics, the world's annual plastic output has reached 400 million tons and is increasing every day. However, the mass production and utilization of plastic products also brings a constant source of environmental pollution. China alone generates more than 70 million tons of plastic waste every year. Not only that, the physical and chemical structure of plastics such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is stable, and it is difficult to decompose in the natural environment, which will cause long-term ecological problems. Therefore, the effective degradation of PET waste has become one of the urgent problems that human society needs to solve today. The PET biodegradation method has the advantages of environmental friendliness and mild conditions, and it is beneficial to improve the biodegradation efficiency of plastics under high temperature conditions. Therefore, the thermophilic PET degradation system has always been the focus of domestic and foreign researchers.
The metabolomics research group led by Cui Qiu, a researcher at the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Processes, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has successfully established a mature gene manipulation platform for C. thermocellum, a typical thermophilic bacterium. Arbitrary genetic transformation to achieve the targeted creation of highly efficient whole bacteria catalysts. At present, researchers have successfully applied the whole-cell catalysis technology based on Clostridium thermocellum to the field of lignocellulose biotransformation and established a new integrated biosaccharification technology. Based on this, the metabolomics research team collaborated with the Uwe T. Bornscheuer team at the University Greifswald in Germany to carry out research in the field of plastic biodegradation and established the most efficient whole bacteria PET known to date The plastic degradation strategy confirms the superiority and application prospect of the thermophilic whole bacteria catalytic strategy. The research results were published in Microbial Biotechnology, an international journal in the field of applied biology, on the subject of Thermophilic whole-cell degradation of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) using engineered Clostridium thermocellum on April 28. PhD student Yan Fei is the first author of the paper, associate researcher Liu Yajun, researcher Cui Qiu, and associate professor Wei Ren of the Greifswald University in Germany are co-corresponding authors.
The researchers used Clostridium thermocellum as the chassis cell to heterologously express the thermophilic cutinase LCC from the genome of the branch and leaf compost element in Clostridium thermocellum, thus successfully establishing a thermophilic whole bacteria catalyst with PET degradation function 1). The whole-bacteria catalyst can successfully convert 60% of the commercial PET plastic sheets into soluble monomers such as ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid within 14 days at 60 ° C (Figure 2). The degradation performance of this PET with C. thermocellum as a whole-bacterium catalyst was significantly higher than that of the whole-bacterium catalytic system based on mesophilic bacteria and microalgae reported previously. Because Clostridium thermocellum can efficiently degrade lignocellulose by synthesizing fibrous bodies, the whole-bacteria catalytic strategy based on Clostridium thermocellum is also expected to play a huge application potential in the biological recovery of mixed textile waste.
This work was supported by the Strategic Pilot Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province.
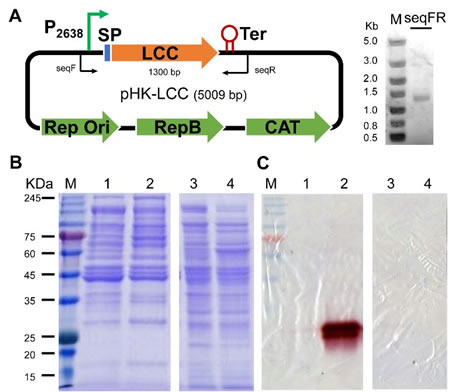
Fig.1 Construction of PET degradation thermophilic whole bacteria catalyst and analysis of LCC activity

Figure 2 Changes in the surface morphology of the PET film during the 14-day incubation with whole-bacteria catalyst
Does the perspex change color?
Perspex, also known as acrylic acid, is resistant to discoloration and fading. Therefore, colored sheets do not fade easily for decades unless it is chemically damaged. Perspex is 92% UV resistant, and a special coating can be applied to make it 98% UV resistant.
Can plexiglass be colored
By adding a small amount of dye during the manufacturing process, the plexiglass can be easily stained with almost any color. However, it is difficult to color plexiglass after production. Consumers should be aware that standard window coloring materials will not work on plexiglass and they must purchase special films to color the plexiglass sheets.

Translucent Acrylic Plexiglass Plastic Sheet
transparent colored acrylic sheets,flexible translucent plastic sheet,translucent acrylic sheet,translucent acrylic panels
Aluminum sheet,Aluminum Composite Panel,Acrylic Sheets,PVC Expanded Plastic Sheet,Polypropylene Hollow Sheets , https://www.decoratepanel.com